Pharma Sector
Table of Content
- Research and development process pipeline in Pharma
- Some Terminology related to Pharma
- Indian Pharma Industry
- References
Research and development process pipeline in Pharma
R&D Process for a new medicine is long and complex. In total it takes 10-15 years to go through the drug discovery and clinical development process and bring a medicine to the market. The process is also costly—the average R&D investment for each new medicine is $1.2 billion, including the cost of failures
The figure below shows the typical R&D process that potential new medicines must go through.
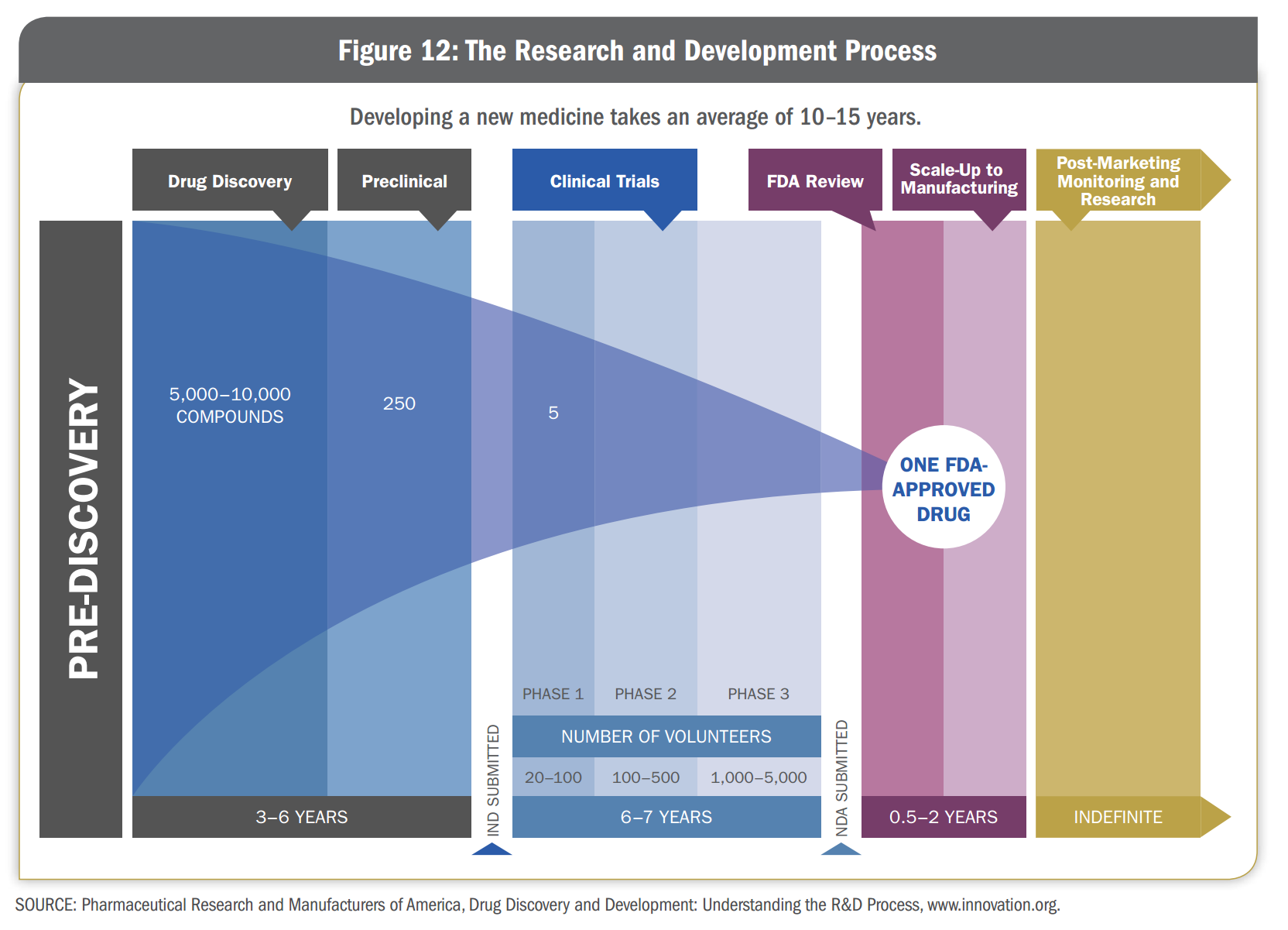
Below are the various steps in the R&D process pipeline to create new medicine
- Drug Discovery
- This involves basic studies to understand the disease as thoroughly as possible - its cause and causes,impact on human body etc. Even at this stage, researchers begin to think about the final product, including its formulation (the recipe for making disease) and its delivery mechanism (whether its taken by mouth, inhaler etc.)
- Preclinical Testing
- Researchers conduct many laboratory studies and tests in animals to determine whether a candidate compound is suitable to be tested in humans. At the end of this process, which can take several years, researchers may have 3-5 compounds deemed to be safe and ready to be tasted in clinical trials. Company submits Investigational New Drug Application to the FDA to seek approval for clinical trials.
-
Clinical Trials
During Clinical Trials compound is tested on human volunteers. It takes typically 6-7 years and involve thousands of participants in several stage of testing.
- Phase 1
- Clinical trials test a candidate medicine in a small group (20 to 100) of healthy volunteers. The main purpose of this trial is to determine the safety of the compound.
- Phase 2
- This involves larger group (100-500) of participants who have the disease or condition under study.
- Phase 3
- Clinical trials test the medicine in a much larger group (1000-5000) of people to generate statistically significant information about safety, effectiveness, and the overall benefit-risk ratio of the medicine. These trials are the longest and can take place at many sites.
- Phase 1
- FDA Review
- If results indicate that a new medicine is both safe and effective, a company submits a New Drug Application (NDA) to the FDA to request approval to market the medicine. FDA carefully reviews all the relevant data and decides whether medicine should be approved.
- Manufacturing
- Approved medicine may be used by millions of people. Planning and scaling up facilities is a highly complicated, long term undertaking.
- Post-Approval Research and Monitoring
- Companies are required to monitor a medicine as long as it is on the market, submitting a periodic reports on safety issues.
Some Terminology related to Pharma
Para Filings
- Para I,II, II, and IV pertain to what is called ANDA filings – Abbreviated New Drug Applications
- Para I, II and III filings all pertain to patent-expired drugs. Non-Litigation category
- Para IV are allowed to be filed – post 5 years of a NCE patent grant by USFDA for a generic version of the Innovator drug
- Para IV First To File (FTF)
- This category can apply for generic version of innovator drug even before 5 years NCE Patent period .
- If approved that company gets an 180 days exclusive approval to market its generic version of the Innovator drug. This can prove very lucrative for the challenger if granted.
- On the other hand there are Litigation Risks where the Innovator tries to prove that the challenger has infringed on its patent/process while developing the generic version
NDA Filings
- 505(b)(2) - Larger Period Exclusivity
- These are meant for biosimilars but completely new products. The FDA in its descretion awards a higher exclusivity period.
GDUFA
- Generic drug user fee Act passed into Law July 2012
- As per this act, generic companies are required to pay user fees to USFDA. This has led to escalation in prices for ANDA Filings. It costs around
Some Pharma Terms
The number of abbreviations in pharma is extensive. Here i have added few terms which i came across during my research for some investing ideas. You can find lot more information here
- Therapeutic Drugs
- groups of drugs that are similar in their chemical structure, pharmacological effect, or clinical use)
- Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (APIs) or bulk drug
- Basic drug itself with desired medicinal properties.
- Pharmaceutical Formulation Intermediates (PFIs) or Direct Compressible
- Involves taking (API) and adding excipients to make a proper blend for the proper finished dosage.
- PFIs require unique manufacturing equipment, machinery is expensive and complex
- Not economically feasible for every drug manufacturer to make their own PFIs
- PFI contribute to 80% manufacturing cost of finished dosage.
- Companies that actively research PFI production will not be able to garner efficiency that are required to create a cost-competitive product.
- Finished Dosage or Formulation
- Form in which drug is consumed by us.
- A dosage form of drug is composed of two things
- API itself
- Excipient
- It is the substance of the tablet, or the liquid the API is suspended in, with other masking, stabilising and binding agent/material
- The main excipient that serves as a medium for conveying the active ingredient is usually called the vehicle.
- Petrolatum and mineral oil are common vehicles
Some regulatory terms
Pharma is a very heavily regulated sector.
Drug master File (DMF)
API manufacturers need to file DMF with regulatory bodies. DMFs are filed with USFDA, MHRA UK, Japan and other country specific bodies for receiving a marketing authorization grant. A DMF provides the regulatory authority with confidential, detailed information about facilities, processes, or articles used in the manufacturing, processing, packaging, and storing of one or more drugs.
- When is DMF Filed?
- When two or more firms work in partnership on developing or manufacturing a drug product.
- The DMF filing allows a firm to protect its intellectual property from a potential partner while complying with regulatory requirements for disclosure of processing details.
- A Formulations player can only use APIs from sources with approved DMFs. Formulation players have to submit samples and documentation for product registration such as ANDA (Abbreviated New Drug Application) using an API source with approved DMFs. It’s difficult to change API partners as it involves a lot of paperwork and re-submissions.
- Use of Intermediates by API suppliers are not regulated.
Indian Pharma Industry
India is the 3rd largest pharma player in the world with 500 different APIs and rank 4th globally in terms of production volumes and 13th globally in domestic consumption value.
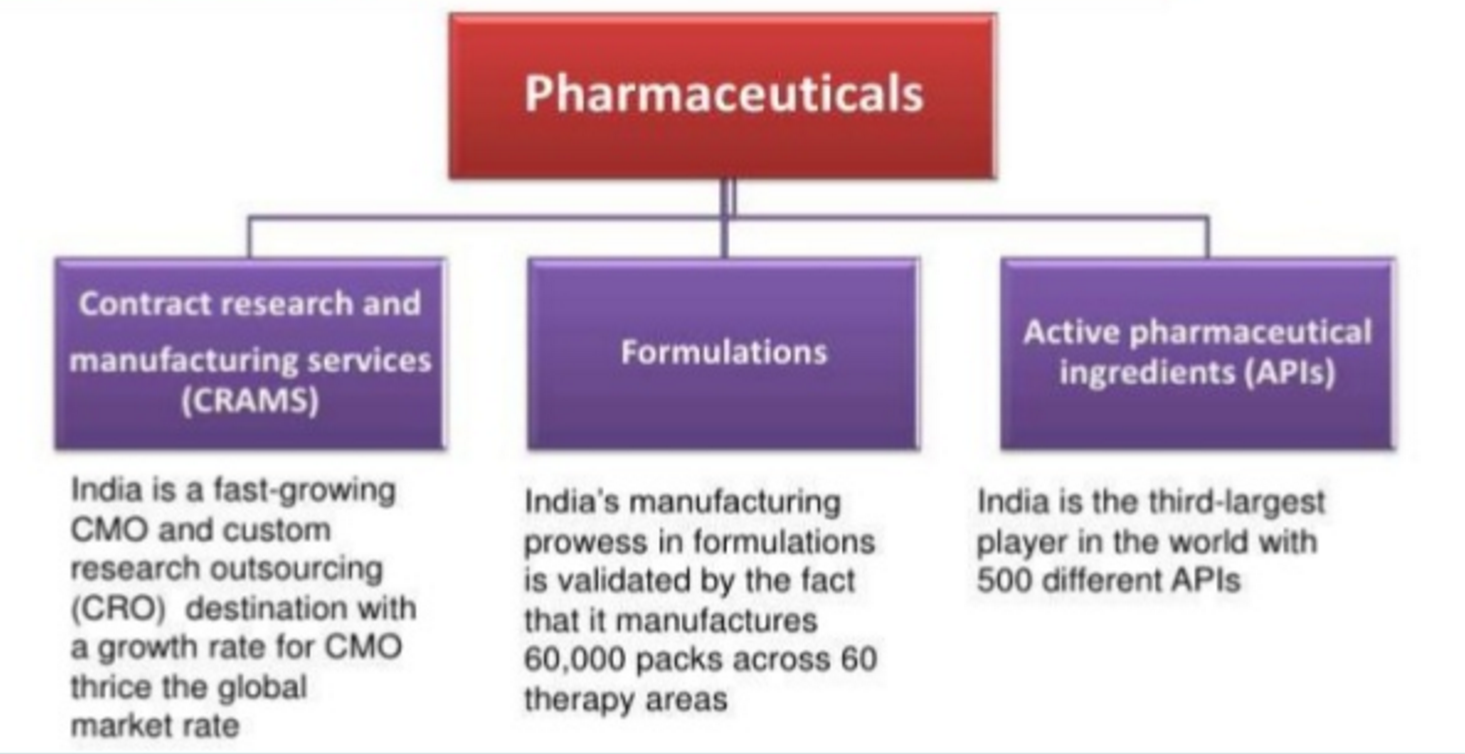
We will look more into Contract Research and Manufacturing Services (CRAMS) .
Contract Research and Manufacturing Services (CRAMS)
CRAMS pertains to outsourcing services/products from low-cost providers. Pharma Multinationals have traditionally been outsourcing intermediates, API’s and Formulations.
CRAMS essentially consists of following two activities :
- Contract Research
- Contract Manufacturing
The image below shows the CRAMS value chain:
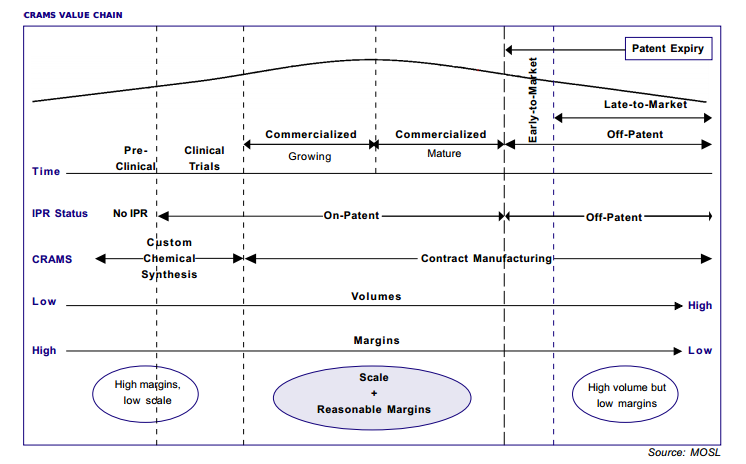
Contract Research
Contract Research includes custom chemical synthesis and clinical trials. Over the last decade, the need to outsource for Big Pharma companies has increased considerably.
Some key factors for Contract research outsourcing :
- Time and quality
- Availability of manufacturing capacity
- Sufficient capacity is key to the new business especially for contract manufacturing. Innovator companies generally request rapid turnaround time.
- Reputation and track record:
- If the CRAMS player was the service provider for the innovator company in the past, and had delivered satisfactory services, the customer will most likely opt for the same CRAMS player for similar or new projects on the basis of the trust that has been built.
- Array of services offered:
- Generally, innovators like to get maximum possible services from same contract research
- Reliability and flexibility:
- Suppliers should be reliable in terms of dedicated management team, financial stability,
- Strong track record of supply, manufacturing, logistics, etc.
- Flexibility is also extremely important to innovators:
- Scalability:
- Pharmaceutical customers prefer suppliers who have the ability to increase their scale of production, as products move from early stages to later stages of drug development.
- Cost:
- Cost is of significant importance for awarding manufacturing contracts especially for products going off-patent.
Contract Manufacturing
Contract Manufacturing involves supply of intermediates, APIs or formulations (for on-patent or off patent molecules)
Some Information for business of Contract manufacturing
Some positives for company doing contract manufacturing:
- Contract manufacturing offers stable revenue stream
- Contract manufacturing offers a very stable revenue stream once the supplies to the innovator commence.
- The contracts are usually valid for at least five years, with confirmed off take from the partners.
- Hence, the contract manufacturer is generally assured of confirmed annual off take on successful commencement of supplies.
- Contract manufacturing also yields decent margins
- Most of the contract manufacturing deals have been struck at 20-25% EBITDA margins.
- The margins will vary from product-to-product and will also depend on whether the supplies are for on patent or off-patent products
- On-patent product supplies are likely to attract higher margins due to the better pricing power enjoyed by the MNC partner in its home market.
- Contract manufacturing assignments are quite long term (valid for at least five years).
Some Negatives:
- Gestation periods are long
- It should also be noted that post the announcement of the contract, it takes 18-24 months for the supplies to begin.
- This is due to the time-consuming registration process with various countries before which supplies cannot commence.
- Significant front-ended capex is involved
- CRAMS players will have to undertake front-ended capex for signing new contracts necessitating strong balance sheets.

Leave a Comment